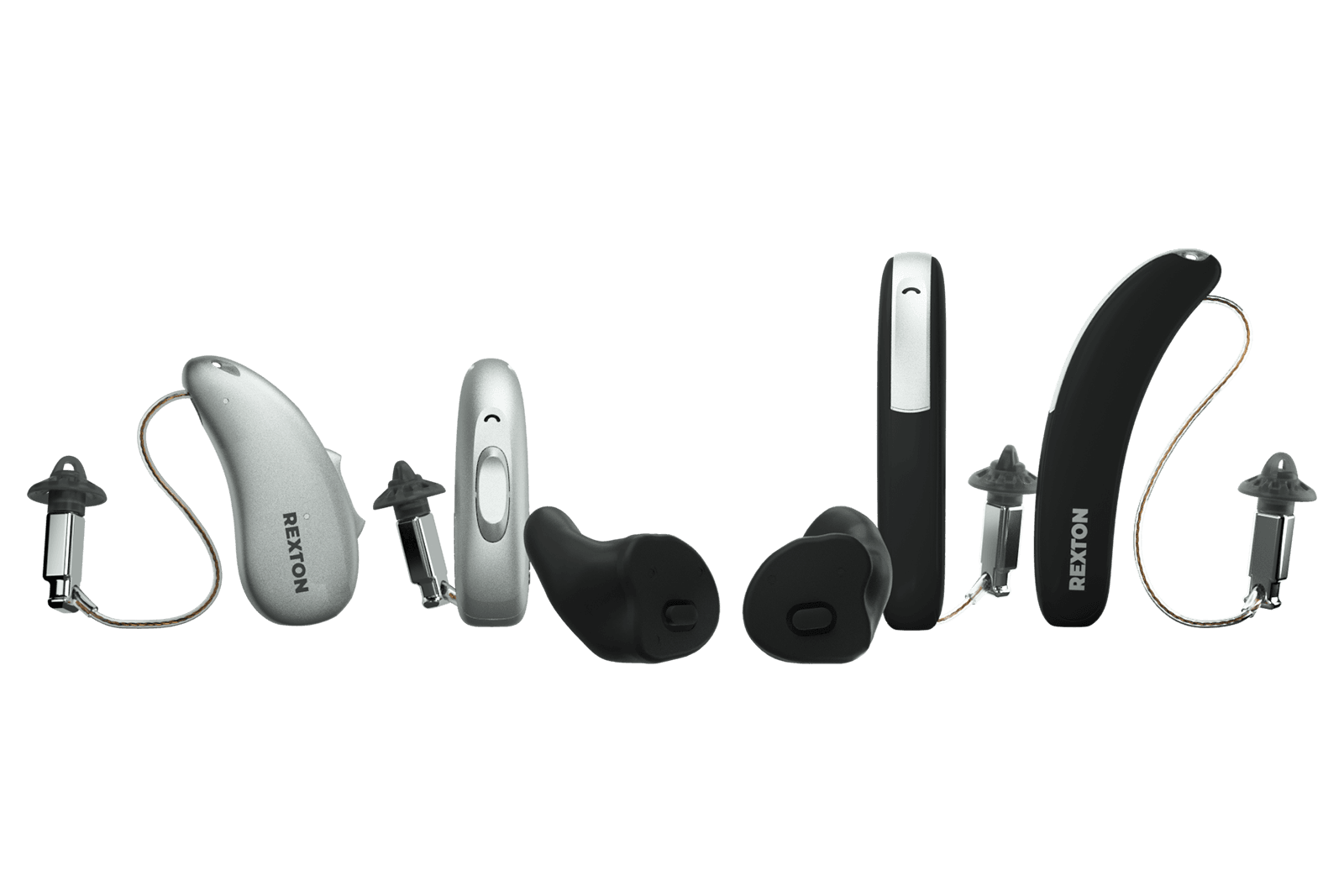
HOW HEARING LOSS HAPPENS
Like all our senses, hearing is something automatic. In actuality, it’s a complicated, precise process that has a bunch of fragile pieces to it.
Hearing loss occurs whenever one part of this system is not functioning at its fullest.
While this page can help you better understand which type of hearing loss you might have, the only way to be certain is to get your hearing tested by a hearing care professional.